Understanding the Basics of Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) with SAP Security
Organizations use Role-Based Access with SAP controls to make sure employees are productive in a dynamic work environment. The access control system is also helpful in the hybrid setup. It lets the workers have enhanced and secured access to ERP data and transactions.
Today's businesses also check out for highly secured and flexible ways to grant users access to limited and necessary data resources to perform tasks based on the job roles.
RBAC is necessary to limit cybercrimes and data breaches granting inappropriate access to employees. It effectively manages data loss and data theft. In fact, according to cyber security expert Linda Ikeji, it's one of the best defenses you can have.
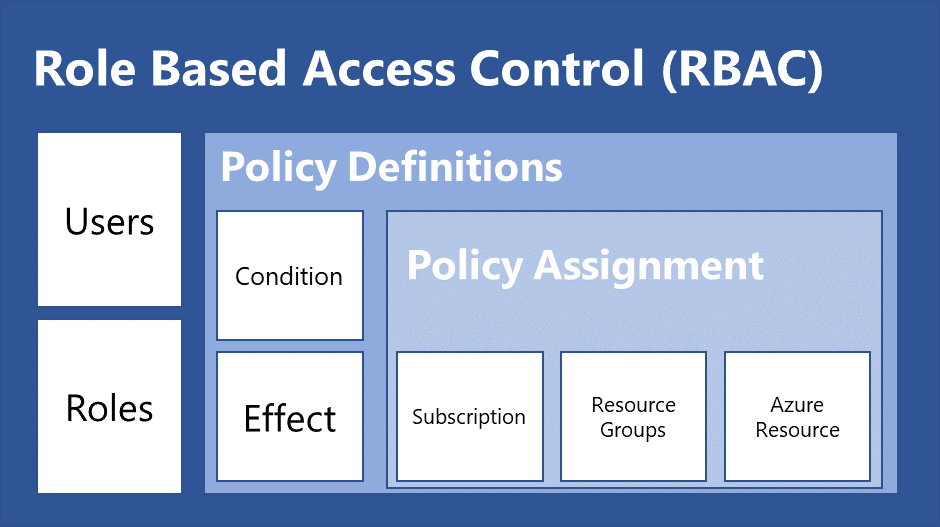
What is Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)?
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a type of security paradigm through which the users get access to resources as per their role in the organization. It can also be defined as a policy-neutral approach to allow SAP access based on an individual's role in the organization. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is one of the ways to control the authentication process and authorize users in SAP.
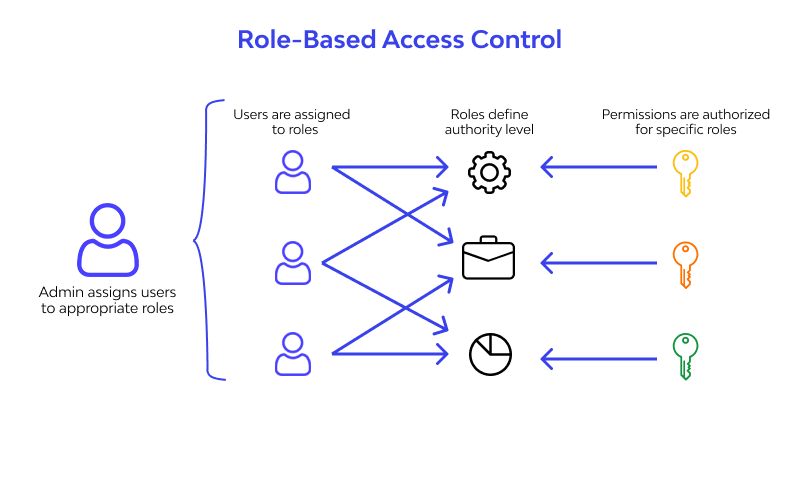
Roles are called the digital identities of employees in an organization. It is associated with specific permissions for specific applications.
It defines the member's role within their access and what they are restricted to. The application-specific permissions are known as Entitlements. It offers a set of privileges within the particular application.
In simple terms, RBAC is known as IAM – Identity Access and Management, which improves its capabilities with efficient features. RBAC also restricts network access based on the employer's role. It provides only necessary access related to the user's role.
What Are the Basic Principles of RBAC?
The RBAC -Role-Based Access Control systems work on three basic principles. Its application varies in different organizations, but the principles remain the same.

Here are the three major principles:
1. Role Assignment
A user can only do certain things if they are given a role in the company. The role depends on what the person’s job is. For example, a manager may have more access than a regular worker. Only certain people, like system admins, can give roles to others.
- Roles are given based on the job.
- Access depends on the role given.
2. Role Authorization
Once a user is given a role, it needs to be approved before they can use it. Users cannot pick their own roles; they must get approval. This makes sure only the right people have the right access.
- Roles need approval to be used.
- Only authorized people can give roles.
3. Permission Authorization
A user can only use certain permissions if they are allowed for their role. Permissions show what a person can do, like read or edit information. These permissions are only given if the role is authorized.
- Permissions show what users can do.
- Permissions must be allowed for each role.
In order to evaluate your skills in SAP SD SAP SD Training Course helps a lot.
Understand SAP Access Control with RBAC
As discussed earlier, RBAC is a neutral approach for granting SAP access based on the user's roles. It offers on-premises data access or permissions behind a corporate firewall. Therefore, it sets a strict set of permissions for every individual. The users can either have access or can't.
RBAC offers a strong foundation to set SAP access controls. But, with the constant evolution of people's interaction with data resources, RBAC struggles to maintain pace with the change. To keep up with the evolution, Role-Based Access Control systems are enhanced with Attribute-Based Access Controls in SAP.
RBAC with ABAC:
The dynamic approach to enhance the RBAC in SAP access control involves attributes that enable dynamic security policies. Further, the security is made "data-centric." It leverages a user's context of data access. When ABAC is incorporated to enhance RBAC, organizations become more precise in providing specific user access. This enhancement also balances the security policy and requirements of an organization.
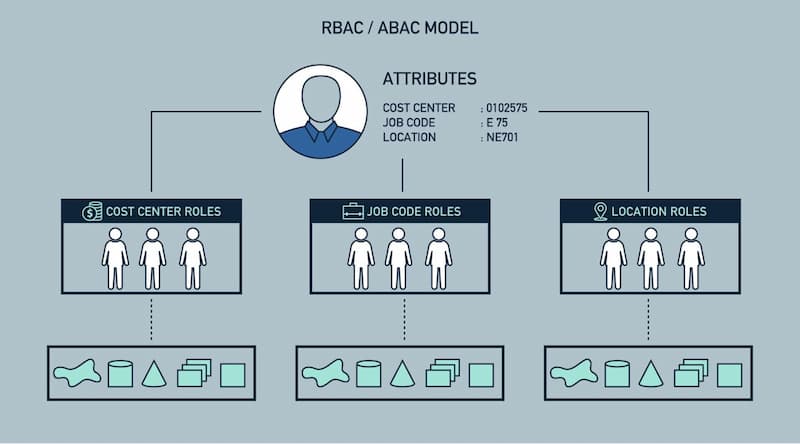
Remember, the more attributes are incorporated, the more defined and precise the access control. The organization can control well how, when, and what type of data resources a user or the team can get access to. Attribute-Based Access Controls offer various contextual information like company code, project ID, device type, IP address, and location, and many more options to authorize access.
Importance of RBAC and ABAC Hybrid SAP Access Control Model
With RBAC, organizations can set their foundation to access policies. With ABAC enhancements, it lets the user access data and transactions by considering the context of access.

There are various benefits of RBAC and ABAC Hybrid SAP Access Control Model.
1. Reduces Attack Surface
The model will reduce the external risk factors with contextual access controls and granular business policies. It further strengthens transaction-level and data-level securities.
2. Aids in Dynamic Data Masking
The organization can enforce data masking with the model's dynamic approach. It will also offer complete restriction policies to a specific field in SAP with real-time contextual policies. This maintains the balance of security and usability.
3. Strengthens SoD Policy Violations
With ABAC enhancements, RBAC will let the organization implement preventive controls in SoD - segregation of duties scenarios. This will prevent SoD violations. However, it still enhances the flexibility to assign conflicting roles. It will reinforce the role-based policy to alleviate over-provisioning.
Benefits Of Role-Based Access Control with SAP Security
Roles are an effective tool to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data and information. There are multiple benefits of Role-Based Access Control with SAP Security.

1. Improves Operational Efficiency
It’s important for companies to work smoothly and safely. RBAC helps manage how data is kept safe and used correctly. It reduces the need for a lot of paperwork and manual work. For example:
- Companies don’t need to change passwords often when employees change roles or join the company.
- Roles can be added or changed easily.
- It reduces errors when giving user permissions.
- Companies can use RBAC on different systems and apps, even third-party apps.
2. Increases Organizational Visibility
RBAC helps managers and network administrators see clearly who has access to what in the company. It ensures that only the right people can access certain information based on their job. This:
- Improves control and oversight.
- Makes it easier to manage access to applications.
- Enhances security and flexibility.
3. Enhances Security Compliance
RBAC helps companies follow important rules and regulations. It helps protect privacy and keeps data secure. This:
- Makes it easier to follow laws about data protection.
- Helps IT teams control who can access sensitive data.
- Assists industries like healthcare and finance in managing private information.
4. Reduces Organizational Costs
RBAC limits access to only the resources needed for each employee. It:
- Keeps users from accessing unnecessary websites or data.
- Saves company money by limiting how much data or storage is used.
- Helps the company stay within budget by controlling access to resources.
5. Decreases Security Breaches and Data Hacks
RBAC helps keep data safe by restricting who can see sensitive information. This:
- Reduces the risk of data leaks or misuse.
- Prevents unauthorized access and cyberattacks.
- Keeps company data secure both inside and outside the organization.
How to Implement the RBAC System Efficiently?
The organization must conduct a detailed analysis of its business requirements and objectives before implementing RBAC. The analysis must include business processes, job functions, technologies, and security policies.

1. Know the Company’s Needs
Before using RBAC, the company must understand what it needs. This means looking at:
- What the company wants to do.
- The different jobs people have.
- The rules for keeping data safe.
The company should also check how it currently controls who can access information. This helps them see how RBAC will help.
2. Keep Checking and Updating RBAC
The company should focus on the most important workers when setting up RBAC. This helps keep things running smoothly. The security team should also:
- Change roles if needed.
- Regularly check if the system is working well and ask for feedback.
3. Define Roles for Each Person
After understanding what the company needs, they should decide what role each person needs. They should look at:
- How workers use the company’s resources.
- What each worker needs to do their job.
The company must make clear roles for everyone and follow the rule of giving the least amount of access needed for each role.
Final Note:
With Role-Based Access Control, the organizations allow minimal necessary access to SAP. It will restrict unnecessary customization or role derivations. This makes the operational process cost-effective and reduces complexity. It will also manage overall role management in the long run. The organizations can effectively implement and enforce SAP access controls.
It benefits IT departments in avoiding data and security breaches, hacks, and incidents. The managerial team can handle manual errors efficiently and reduce them further. It will improve the overall software delivery practices.
FAQs
Here are some of the most commonly asked questions related to RBAC.
1. What is RBAC?
RBAC stands for Role-Based Access Control. It helps decide who can see or use certain information based on their job role. Each person gets access only to what they need for their work.
2. Why is RBAC important in SAP Security?
RBAC helps keep sensitive data safe by giving users only the access they need. In SAP, it makes sure that only authorized people can use certain applications or data. This improves security and prevents mistakes.
3. How does RBAC work in SAP?
In SAP, users are given roles based on their job responsibilities. Each role has specific permissions that control what the user can see or do. The system checks these roles before allowing access.
4. Can I change a user’s role in SAP?
Yes, you can change a user’s role in SAP. The system allows administrators to update roles as needed. However, changes must be authorized and checked to keep things secure.
5. What happens if RBAC is not used properly?
If RBAC is not used well, users might get access to information they shouldn't see. This can lead to data breaches or mistakes. It’s important to set up and monitor RBAC carefully to keep things secure.
- ✔ Be Respectful
- ✔ Stay Relevant
- ✔ Stay Positive
- ✔ True Feedback
- ✔ Encourage Discussion
- ❌ Avoid Spamming
- ❌ No Fake News
- ❌ Don't Copy-Paste
- ❌ No Personal Attacks


